
MongoDB, Inc. today revealed it has acquired Voyage AI, a provider of embedding models and rerankers that make it possible to build more accurate generative artificial intelligence (AI) applications
Scheduled to be more tightly integrated with the MongoDB document and vector databases later this year, the Voyage AI models will enable application developers to build AI applications that can be reliably deployed in, for example, the financial services and healthcare sectors, says Andrew Davidson, senior vice president of products for MongoDB.
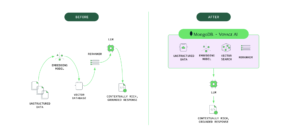
The embedding and reranking tools created by Voyage AI in effect streamline the retrieval augmented generation (RAG) workflows that organizations are relying on to extend the capabilities of a large language model (LLM). In absence of that capability, application developers are not able to confidently minimize the hallucinations that might otherwise be generated by LLMs that are inherently probabilistic, he adds.
In general, MongoDB provides application developers with access to a document database that enables them to store data in self-describing schema-less format that flexibly provides a lot more context. That database then provides the foundation needed to integrate a vector database that exposes that data to an LLM.
The embedding models and rerankers created by Voyage AI makes it possible to ensure that the data being surfaced more precisely aligns with the application use case by extracting meaning from highly specialized and domain-specific text and unstructured data, notes Davidson. “It provides greater fidelity,” he says.
That’s critical because without it, IT organizations are going to continue to be hesitant to deploy AI applications that generate outputs that can be trusted, Davidson adds.
Additionally, Voyager AI makes available AI models for specific vertical industries that can be further customized to accelerate the building of AI applications used to incorporate legal and financial documents, images, code, or an entire knowledge base without each development team having to reinvent the same embedding and reranking tools.
It’s not clear at what pace organizations are operationalizing generative AI, but the one challenge all of them seem to encounter is how to expose the right data to the right model at the right time. MongoDB is essentially making a case for using an abstraction that is familiar to both application developers and database administrators (DBAs) that will collaboratively need to build, deploy, update and manage AI applications.
That’s crucial because as the backlog of AI applications that need to be deployed in production environments continues to build, the level of tolerance for devoting time and resources to data management tasks and processes is only going to decline. Many senior-level executives are rapidly losing patience as realizing the promise of AI continues to elude them largely due to data management issues that many of them don’t really understand. The one thing that is certain is despite that level of knowledge, it won’t be long before many of those leaders start to wonder if the IT teams they have in place are actually up to the AI challenge at hand.

